What Are Three Zones Used to Describe Water's Depth
Groundwater -- 1 water that flows or seeps downward and saturates soil or rock supplying springs and wells. The abyssal zone which is that area that lies below the reach of sunlight and is always dark and finally the Benthic zone which is at the sea bottom itself.
Movement of water into soil is called infiltration and.
. Littoral limnetic and pro-fundal. 2 Water stored underground in rock crevices and in the pores of geologic materials that make up the Earths crust. Lentic waters are generally divided into three zones or sub-habitats.
3280 to 13000 ft below the sea surface Abyssopelagic zone. Water moves because of water potential gradients in the soil caused mostly by gravity salt content and water usage and the direction of flow is from a zone of. And the deep zone contains cold high-density water that accounts for 80 percent of.
Sea lettuce Ulva lactuca is a type of green algae commonly found in tidal pools. Green algae can be found in marine or freshwater habitats and some even thrive in moist soils. The aphotic zone incudes.
This layer extends from 6000 meters 19686 feet to the. The upper layer of the soil is the unsaturated zone where water is present in varying amounts that change over time but does not saturate the soil. - the ocean is layered according to density and consists of a shallow surface mixed zone a transition zone and a deep ocean zone - this doesnt exist in high latitudes because there is no rapid change in temperature or density with depth.
The term groundwater is used to describe this area. Hadalpelagic Zone - Beyond the abyssopelagic zone lies the forbidding hadalpelagic zone. The deeper you swim into ocean the greater water pressure pushes down on you.
This article throws light upon the three main types of movement of water in soil. These algae come in three forms. Most of these are invertebrates such as basket stars and tiny squids.
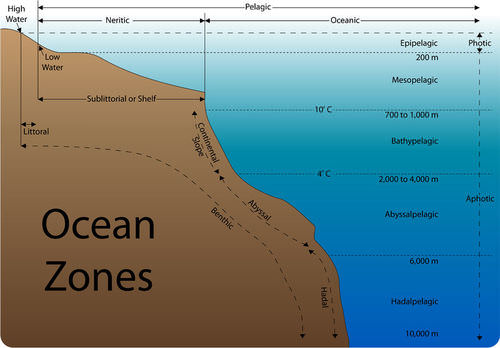
They are the intertidal zone the area that is periodically covered by tidewaters. The top layer of the Earths surface consisting of four major components. The water above the continental shelf is the neritic zone.
Soil water is used by plants in life functions and transpiration but it also can evaporate directly to the atmosphere. There are three main layers in the ocean based on water density which varies with temperature and salinity. A small pond may consist entirely of littoral zone.
The first zone is epipelagic zone the second is mesopelagic zone the third is bathypelagic zone the fourth is abyssopelagic zone and the last one is hadalpelagic zone. This zone contains all the habitats of the sea bottom whether in coastal. Inner shelf closest to the continent outer shelf along the outer edge of the continental shelf next to the continental slope bathyal zone on the continental slope averaging between 200 to 3-6000 meters abyssal zone on the abyssal plain the relatively flat deep-sea.
Tide pools estuaries mangrove swamps and rocky coastal areas are all part of the intertidal zone. Air water organic matter and mineral matter. The intertidal neritic and oceanic.
Depth Zone Depth m Pressure Range atm Average Temperature ºC Light Intensity. THE WATER TABLE The depth to the water table can be determined by installing wells that penetrate the top of the saturated zone just far enough to hold standing water. And the hadopelagic hadal zone is 6000 meters and deeper.
The pelagic or the open water zone. There are three categories of soil particles--sand silt and clay--which are called soil separates acts as a sponge to take up and retain water. More than 4000 species of green algae exist on the planet.
The ocean is divided into horizontal zones based on the depth of water beneath. Water beneath the land surface occurs in two principal zones the unsaturated zone and the saturated zone Figure A-1. The intertidal zone is the area of the seafloor between high tide and low tide.
The ocean is divided into different depth zones. The deepest fish ever discovered was found in the Puerto Rico Trench at a depth of 27460 feet 8372 meters. The most important vertical distinction in the oceans is between the small surface zone that has light the photic zone and the entire rest of the ocean without light the aphotic zone.
In the unsaturated zone the voids--that is the spaces between grains of gravel sand silt clay and cracks within rocks--contain both air and water. With the water depth it also gets influence from pressure. 500 to 3280 ft below the sea surface.
The word comes from the Greek terms pélagos open sea and epí upon. The warm surface mixes layer accounts for only 2 percent of ocean water. 20000 to 35000 ft below the sea surface.
This upper layer which is influenced by light is especially productive because the primary producers algae cyanobacteria and seagrass. Summary of depth zones. However a deep lake with an abruptly sloping basin may possess an extremely reduced littoral zone.
13000 to 20000 ft below the sea surface Hadal zone. The epipelagic extends from the water surface down to a depth of 200 metres. This zone is further subdivided by depth as follows.
The upper surface of the saturate zone is called the water table. Below this layer is the saturated zone where all of the pores cracks and spaces between rock particles are saturated with water. The bathypelagic midnight zone between 1000-4000 meters.
Three-quarters of the ocean floor lies within this zone. Most benthic habitats are associated with the bottom of the ocean and are distinguished by depth as follows. The transition zone includes the thermocline and the pycnocline and accounts for 18 percent of ocean water.
It bridges the gap between land and water. The division labeled aphotic zone contains this additional text. Depth zones of the ocean.
The shallow zoneAt shore open water zonelocated away from shore and deep water zonebelow the open water zone. The abyssopelagic abyss zone between 4000-6000 meters. Preparation of a water-table.
Unicellular colonial or multicellular. Epipelagic Mesopelagic Bathypelagic Abyssopelagic Hadopelagic.

Pelagic Zone Definition Location Depth Animals Facts Britannica

0 Response to "What Are Three Zones Used to Describe Water's Depth"
Post a Comment